WellHealthOrganic.com provides information on the health benefits and nutritional sources of vitamin E. Vitamin E is a nutrient found in a variety of foods, including oils, nuts, seeds, and vegetables. It has been linked with a number of health benefits, including reducing the risk of heart disease and cancer.
Introduction: The Importance of Vitamin E for Good Health
Vitamin E is a powerful antioxidant that plays an essential role in maintaining good health. It has numerous benefits, including reducing the risk of heart disease, boosting immune function, protecting against cancer and other chronic diseases, and promoting healthy skin and hair.
Due to its antioxidant properties, vitamin E works by neutralizing free radicals in the body that can cause cell damage and contribute to disease development. It also helps prevent the oxidation of low-density lipoprotein (LDL) cholesterol, which is a major risk factor for heart disease.
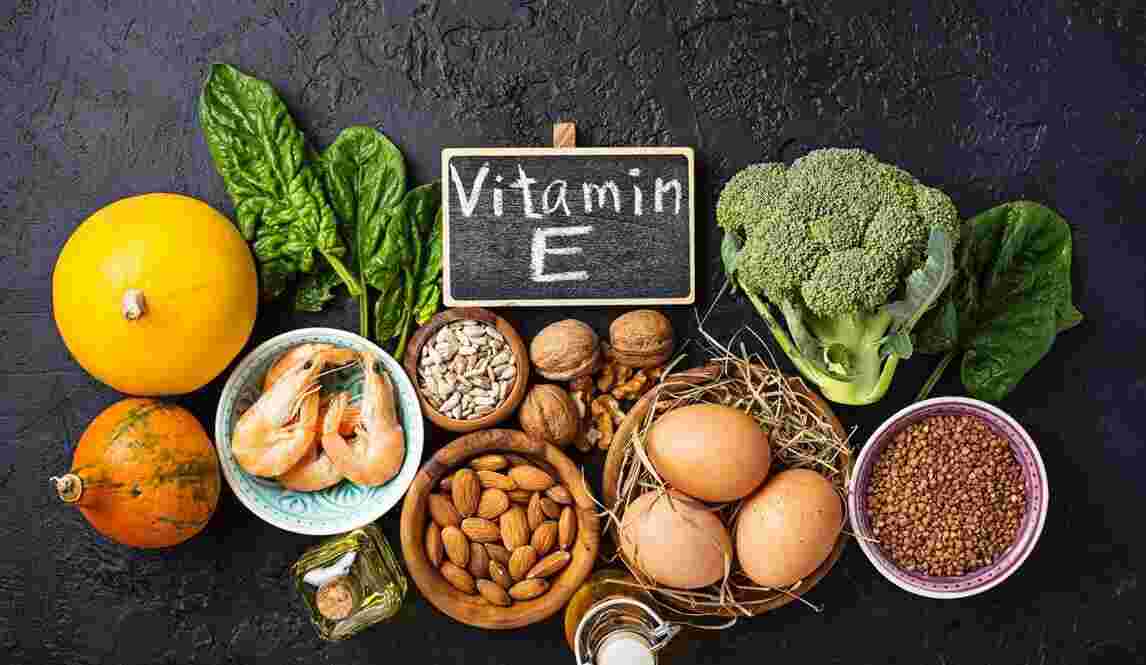
Vitamin E is found naturally in many foods, including nuts and seeds, vegetable oils, leafy green vegetables like spinach and kale, whole grains and fortified breakfast cereals. However, some people may need to supplement with vitamin E if they have certain medical conditions or are not getting enough through their diet.
Also Read: WellHealthOrganic.com: Weight Loss in Monsoon – These 5 Monsoon Fruits Can Help You Lose Weight
Understanding Vitamin E: Types and Functions
Vitamin E is a fat-soluble vitamin that has multiple forms, including tocopherols and tocotrienols. The most biologically active form of vitamin E is alpha-tocopherol, which has the highest antioxidant activity among all the vitamin E forms. Along with its antioxidant properties, vitamin E also plays an essential role in maintaining healthy skin, hair, and eyes.
One of the primary functions of vitamin E is to protect cells from oxidative damage by neutralizing free radicals in the body. This function helps to prevent chronic diseases such as cancer, heart disease, and Alzheimer’s disease. In addition to its antioxidant activity, vitamin E also supports immune function by enhancing the production of natural killer cells and improving their ability to fight off infections.
Vitamin E can be obtained from a variety of food sources such as nuts, seeds, leafy green vegetables, and vegetable oils like sunflower oil or olive oil. However, some people may have difficulty getting enough vitamin E through their diet alone and may need to consider supplementing with it instead. Overall, understanding the types and functions of Vitamin E is important for maintaining optimal health and preventing various illnesses caused by oxidative stress in our bodies.
Health Benefits of Vitamin E: From Immunity to Skin Health
Vitamin E is an essential nutrient that plays a crucial role in maintaining good health. One of its most well-known benefits is its ability to boost the immune system. Studies have shown that vitamin E can improve the body’s ability to fight off infections, reduce inflammation, and protect against various diseases.
In addition to boosting immunity, vitamin E also has numerous benefits for skin health. It is a powerful antioxidant that can help protect the skin from damage caused by free radicals and environmental factors such as UV radiation and pollution. Vitamin E also helps promote healthy skin by improving moisture retention and reducing inflammation.
Furthermore, vitamin E has been linked to several other health benefits such as improved eye health, reduced risk of heart disease, and even potential cancer prevention properties. Some dietary sources of vitamin E include nuts, seeds, vegetable oils, spinach, and broccoli. Incorporating these foods into your diet can help ensure you are getting enough of this important nutrient for optimal health.
Also Read: wellhealthorganic.com:diet-for-excellent-skin-care-oil-is-an-essential-ingredient
How Much Vitamin E Do You Need? Recommended Daily Allowance
The recommended daily allowance (RDA) for vitamin E varies depending on age and gender. For adult men and women aged 14 years and older, the RDA is 15 milligrams (mg) or 22.4 international units (IU). However, for infants and children, the RDA is lower ranging from 6 to 11 mg per day.
Vitamin E can be found in a range of foods such as nuts, seeds, vegetable oils, leafy greens, and fortified cereals. Consuming a balanced diet that includes these sources can provide enough vitamin E to meet your daily requirements. But if you’re not getting enough through your diet alone or have certain health conditions that affect absorption of fat-soluble vitamins like vitamin E, supplementation may be necessary.
It’s important to note that excessive intake of vitamin E supplements could have harmful effects on the body such as an increased risk of bleeding. Thus it’s best to consult with a healthcare provider before taking high doses of any supplement including Vitamin E.
Natural Food Sources of Vitamin E: Plant-Based vs. Animal-Based
Vitamin E is a fat-soluble nutrient that plays an essential role in maintaining healthy skin, eyes, and immune system. There are two types of Vitamin E compounds—tocopherols and tocotrienols. However, the most common form of Vitamin E found in our daily diet is alpha-tocopherol. In this article, we will compare natural food sources of Vitamin E from plant-based and animal-based sources.
Plant-based foods such as nuts (almonds, peanuts), seeds (sunflower seeds, pumpkin seeds), vegetable oils (wheat germ oil, sunflower oil), green leafy vegetables (spinach and broccoli) are some excellent natural sources of Vitamin E. Besides these food items, fruits such as avocado and mangoes also contain high levels of Vitamin E. Plant-based foods are not only abundant in antioxidants but also provide a wide range of nutrients like dietary fiber, vitamins (A,C,K), minerals such as iron and calcium.
Animal products like egg yolks, fish oils (salmon or trout), fortified cereals can be good sources for obtaining vitamin E compounds. While animal-based products have lesser amounts compared to plant-based sources for vitamin E intake; it’s important to note that they do come with other nutritional benefits – including omega-3 fatty acids which helps reduce inflammation within the body.
Also Read: 8 Beauty Benefits of Using Ice cells On The Skin
Top 10 Vitamin E-Rich Foods You Should Include in Your Diet
Vitamin E is a crucial nutrient that helps protect cells from damage caused by free radicals. It also plays an essential role in the immune system, DNA repair, and other important bodily functions. Eating a balanced diet that includes vitamin E-rich foods can help ensure you meet your daily requirements of this vital nutrient.
Some of the top vitamin E-rich foods include nuts such as almonds, hazelnuts, and peanuts. These nuts are not only rich in vitamin E but also provide healthy fats, fiber, and protein to your body. Other excellent sources of vitamin E include leafy greens like spinach and kale which provide additional vitamins and minerals to support overall health.
For those who prefer incorporating fruits into their diets, fruits such as avocados or kiwis can be great choices since they contain high amounts of Vitamin E per serving. Additionally, fortified cereals are another source of Vitamin E for those with dietary restrictions or preferences that don’t allow them to consume animal products or plants such as wheat germ oil that tend to have high-fat content.
Overall, adding these 10 Vitamin-E rich foods into your diet will help promote better health while ensuring you get enough nutrients to maintain good health over time.
Cooking with Vitamin E: Tips for Maximizing Nutrient Retention
One of the most important vitamins for maintaining healthy skin and hair, Vitamin E is also a powerful antioxidant that can help protect against cell damage caused by free radicals. Cooking with Vitamin E-rich foods can help you maximize your nutrient intake, but it’s important to know which cooking methods are best for preserving this vital nutrient.
One way to ensure maximum retention of Vitamin E in your cooking is to use low heat and avoid overcooking your food. This means sautéing vegetables until they’re just tender or lightly roasting nuts at a low temperature instead of frying them. Additionally, pairing Vitamin E-rich foods with healthy fats like olive oil or avocado can help improve absorption of this vitamin.
Another tip for maximizing Vitamin E retention is to store your food properly before cooking. Keep nuts and seeds in a cool, dry place away from direct sunlight to preserve their natural oils and nutrients. Similarly, storing fruits and vegetables in the fridge can help maintain their nutrient content until you’re ready to cook with them. By incorporating these tips into your cooking routine, you can ensure that you’re getting the maximum benefit from this essential vitamin.
Supplements vs. Whole Foods: Which Is Better for Vitamin E Intake?
Supplements and whole foods both have their pros and cons when it comes to vitamin E intake. Supplements may provide a higher concentration of vitamin E in a more convenient form, but they lack the other nutrients present in whole foods that work together with vitamin E to support overall health. On the other hand, whole foods like nuts, seeds, vegetables and fruits not only contain vitamin E but also many other beneficial nutrients like fiber, antioxidants, and healthy fats.
Research shows that consuming natural food sources of vitamin E reduces the risk of chronic diseases like cancer and heart disease. In contrast, studies on supplement use suggest no significant reduction in mortality rates from chronic diseases such as cancer or cardiovascular disease. Moreover, taking supplements can have negative effects if consumed excessively leading to toxicity symptoms.
In conclusion, while supplements can be helpful for individuals who struggle to meet their recommended daily intake of vitamin E through diet alone; however eating a balanced diet rich in whole foods is always best for optimal health outcomes.
Vitamin E Deficiency: Signs, Causes, and Treatment
Vitamin E is a fat-soluble nutrient that acts as an antioxidant in the body, protecting cells from damage caused by free radicals. However, vitamin E deficiency can lead to various health problems such as muscle weakness, vision disturbances, and impaired immune function. One of the most common causes of vitamin E deficiency is malabsorption, which can occur due to digestive disorders like celiac disease or pancreatic insufficiency.
The symptoms of vitamin E deficiency may vary depending on the severity and duration of the deficiency. In mild cases, individuals may experience fatigue, dry skin or hair loss. Severe deficiencies can result in neurological symptoms such as numbness or tingling in hands and feet. To treat vitamin E deficiency, doctors usually recommend taking supplements recommended by them based on their blood test results along with consuming foods rich in Vitamin E such as nuts (almonds), seeds(sunflower), spinach and avocado.
Overall, it’s essential to maintain adequate levels of vitamin E in our diet to prevent any potential health complications associated with its deficiency.
Conclusion: Improving Your Health with WellHealthOrganic.com
In conclusion, WellHealthOrganic.com is a fantastic resource for individuals looking to improve their overall health and wellbeing. With a focus on organic, high-quality supplements and vitamins, the website provides valuable information about the benefits of Vitamin E and its many nutritional sources. By incorporating these sources into your diet or supplement routine, you can effectively support your immune system, reduce inflammation throughout your body, and prevent chronic diseases.
Overall, we highly recommend using WellHealthOrganic.com as a trusted source of information for all things related to natural health and wellness. Whether you are looking to improve your physical fitness or simply want to live a more balanced lifestyle, this website has everything you need to get started. So why wait? Start exploring today and take the first step towards a healthier future!
Frequently Asked Questions About Vitamin E
Q: What are the health benefits of Vitamin E?
A: Vitamin E is a potent antioxidant that protects cells from damage caused by free radicals. It also helps to regulate the immune system and reduce inflammation in the body. Additionally, some studies suggest that taking vitamin E supplements may lower the risk of certain chronic diseases such as heart disease, Alzheimer’s disease, and cancer.
Q: What are some natural sources of Vitamin E?
A: Some foods that are high in vitamin E include nuts (such as almonds and peanuts), seeds (such as sunflower seeds), leafy greens (such as spinach and broccoli), vegetable oils (such as olive oil), and fortified cereals. However, it can be difficult to get enough vitamin E through diet alone, which is why many people choose to take supplements.
Q: Is it possible to have too much Vitamin E?
A: Yes, it is possible to consume too much vitamin E through supplements or fortified foods. This can lead to nausea, diarrhea, headaches, fatigue, blurred vision, and other symptoms. It is important to talk to your healthcare provider before starting any new supplement regimen to ensure you are taking a safe dosage for your individual needs.